Quick Start
The quick start procedures include the following steps:
Tools
RC receiver connection
Firmware setup
Propeller mounting
Manual flight in position mode
1. Tools
Hardware
A computer with Windows 11 or Ubuntu 18.04 installed
Kerloud UAV
Kerloud telemetry
Transmitter
Software
(1) QGroundControl software:
Windows 11:
Baiduyun download link: https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=NJe8LAfI1Qg6n9sEHW54-g Code: da2e
Ubuntu 18.04:
After downloading, users need to execute the following commands to activate the software.
sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER
sudo apt-get remove modemmanager -y
sudo apt install gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-libav gstreamer1.0-gl -y
# Then logout and login again to enable the change to user permissions.
chmod +x ./QGroundControl_flyingrover.AppImage
./QGroundControl_flyingrover.AppImage
(2) Serial port driver for the telemetry (Windows 11 System Only)
Baiduyun download link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1391Qkr-uLmmnIo6WG9F6qg Code: gw84
2. RC Receiver Connection
The RC receivers and transmitter are not provided in the default Kerloud UAV package, and users are advised to choose those supporting the SBUS protocol. We have to connect the RC receiver with the Pixhawk first, and a cable is ready for use as shown below.
Users are advised to use a velcro to attach the RC receiver to the airframe, and also pay attention to antennas from the RC receiver so they won’t get damaged by propellers.
3. Firmware Setup:
The onboard flight control unit Pixhawk has been loaded with stable px4 firmware based on V1.10.0, and parameters are tuned well with real flight tests in factory. In most cases, users do not need to change those onboard parameters such as attitude and position control gains. The official setup for px4 can be referred in: https://dev.px4.io/master/en/setup/config_initial.html.
Due to transport vibrations and district differences, users are strongly recommended to conduct sensor calibration for compass, gyroscope and accelerometer sensors to avoid unexpected behaviors. We can easily do so by using the provided micro USB cable or telemetry set to connect the pixhawk with a computer running Qgroundcontrol (QGC) software.
Airframe Setting:
This step is not necessary for quick start. The default airframe for Kerloud UAV products is Generic Quadcopter, depicted as:
Caution
The in-factory parameter settings will be lost if users click the Apply button at the top right, which will lead to degraded performance in flight. Hence this step is not recommended.
Sensor Calibration:
Sensors can be calibrated by following the tips in QGC:
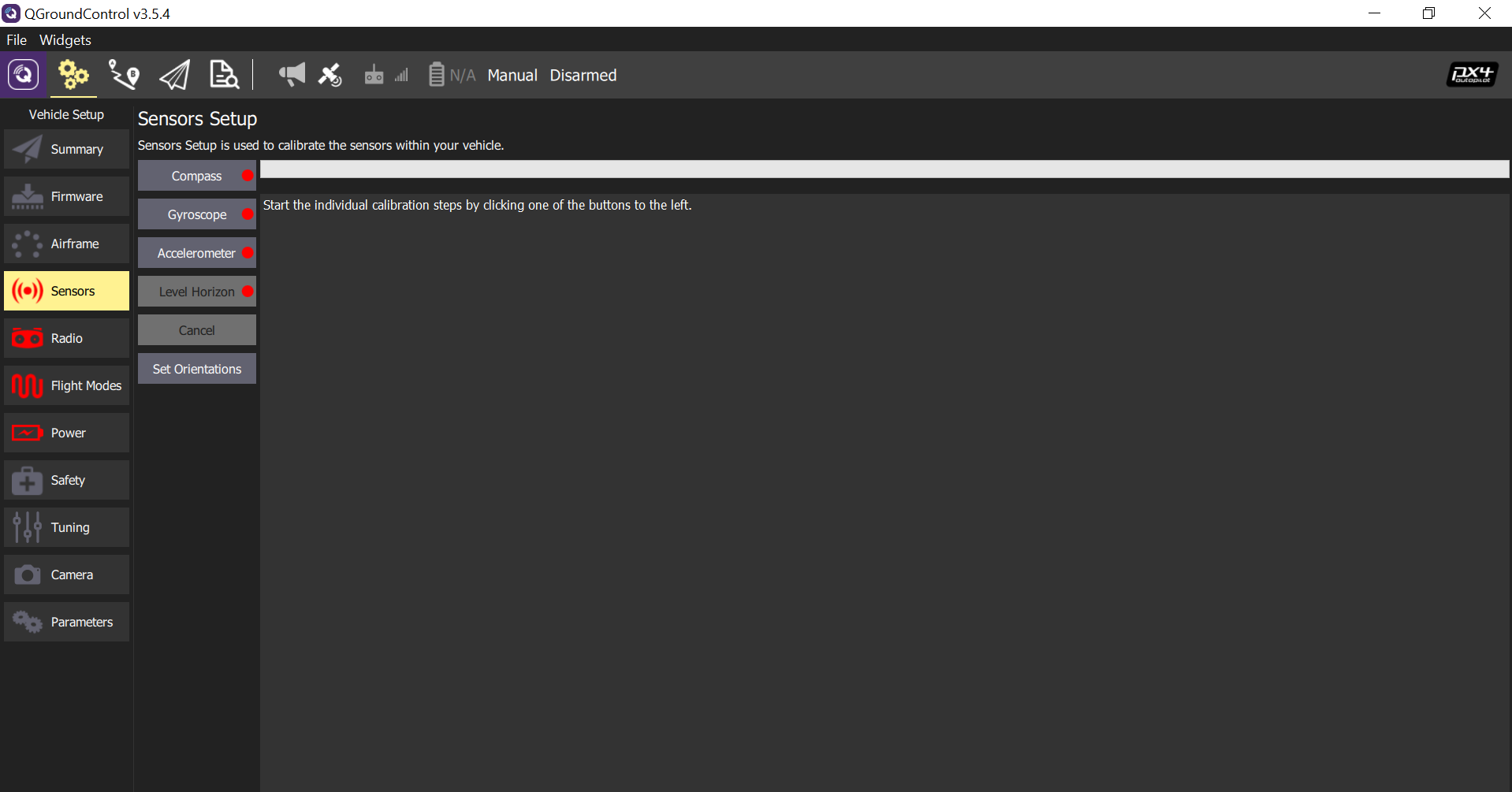
Users are suggested to connect the GPS to the autopilot before compass calibration, as the external compass is equipped in the GPS module, then both the onboard and external compasses will be calibrated. Users should keep the autopilot absolutely static during gyroscope calibration, as even small motion can cause calibration failure or lead to unacceptable gyro bias. The UAV can be placed on flat table surfaces or vertical walls for accelerometer calibration. Hand-hold calibration is not recommended.
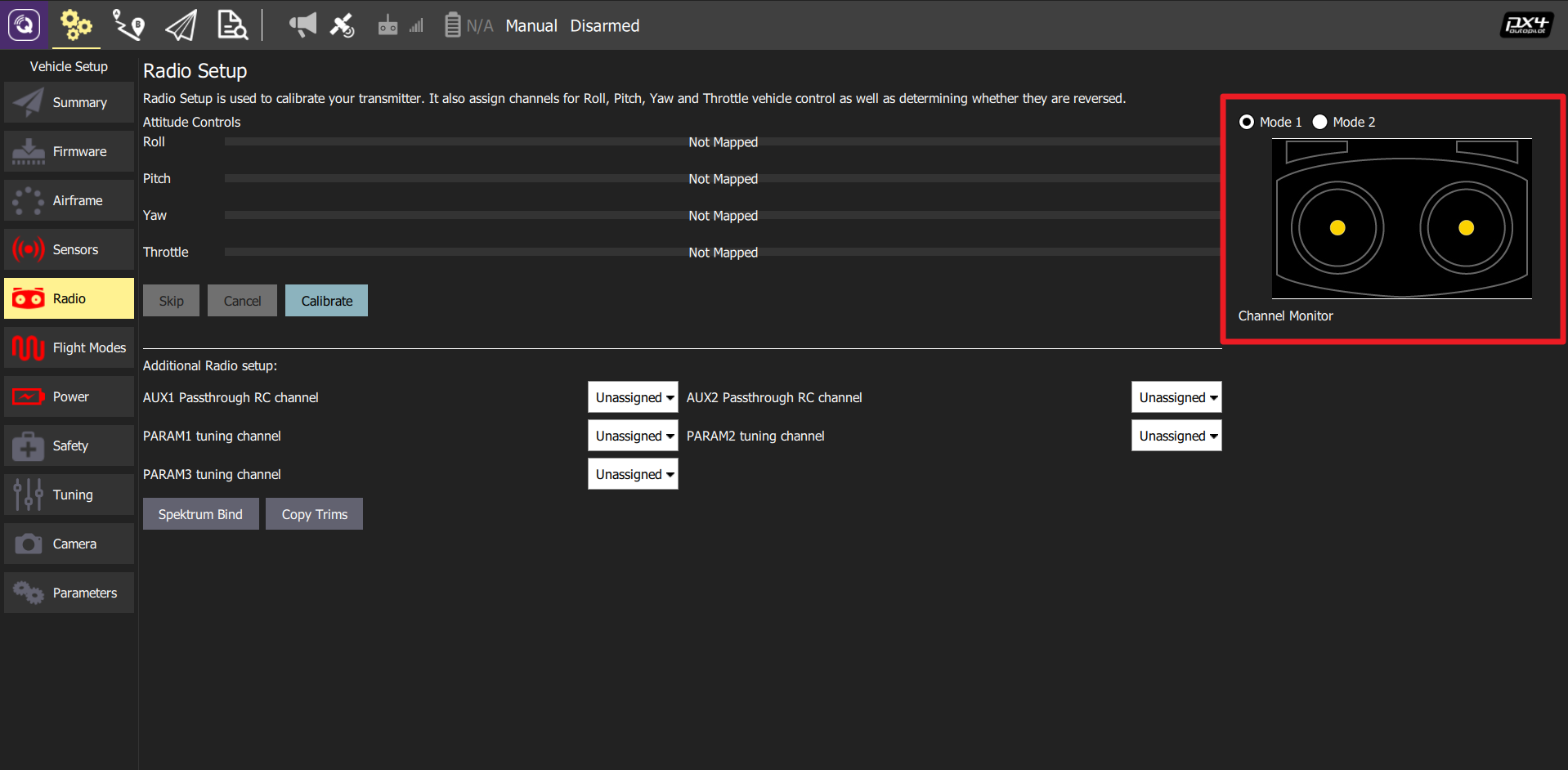
RC Calibration:
We can select either right hand mode (Mode 1, Japanese Hand) or left hand mode (Mode 2, American Hand) for RC operation. By clicking the Calibrate button, users can complete the procedure easily by following QGC commands.
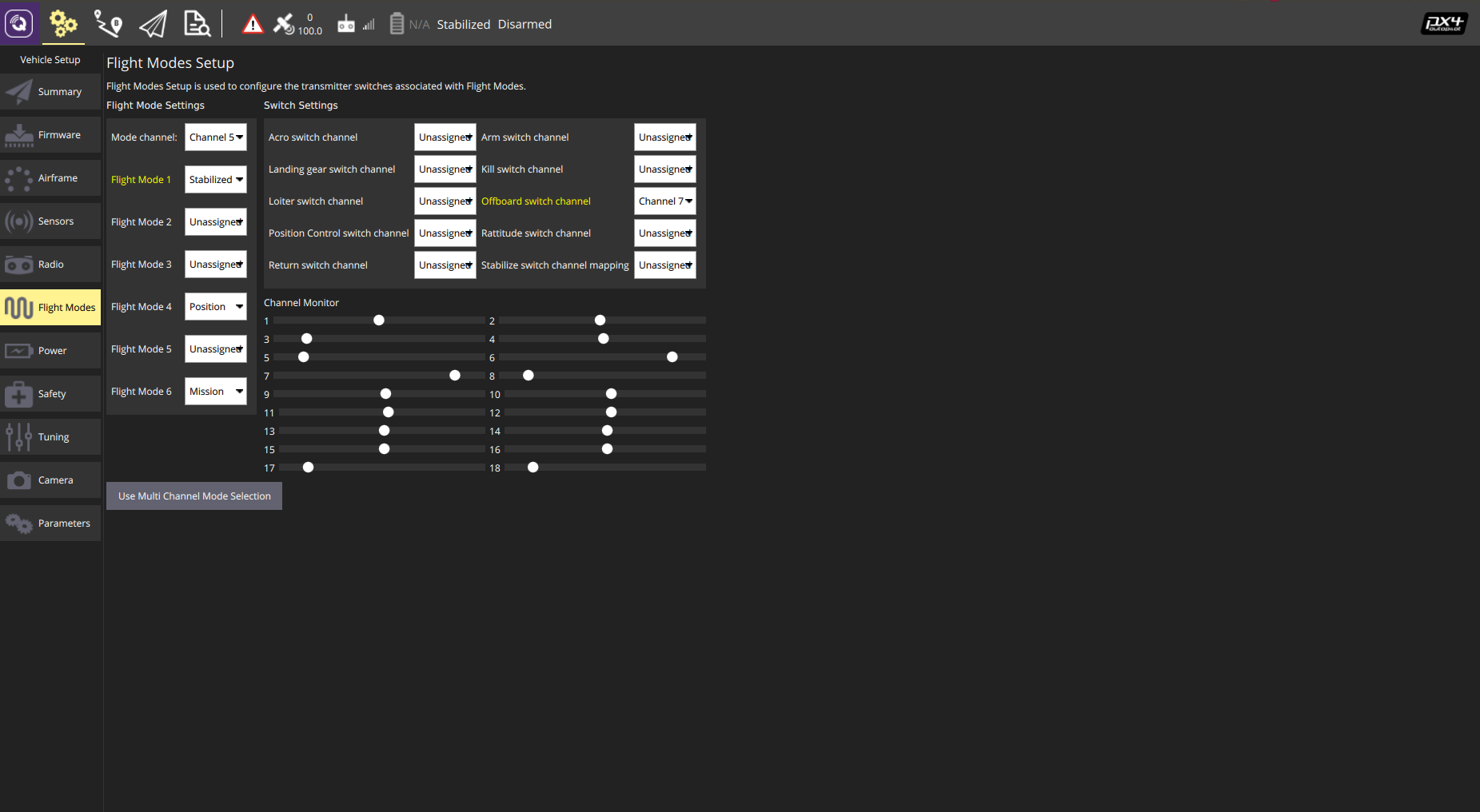
Flight Mode Setting:
Users should allocate one channel (e.g. channel 5) for flight mode setting, and another (e.g. channel 7) for offboard control triggering. Users are suggested to set at least STABILIZED, POSITION and OFFBOARD modes for Kerloud UAV.
The STABILIZED and POSITION modes are used for manual control via the RC transmitter. To highlight here, the STABILIZED mode is for experienced pilots wherein joystick inputs are mapped to the attitude reference, while joystick inputs in POSITION mode are feed into the velocity reference. In the OFFBOARD mode, the uav is commanded by the onboard computer to achieve autonomous tasks such as waypoint flight, trajectory tracking, and visual tracking, etc. Another mode is called MISSION mode, wherein the uav will carry out autonomous waypoint flight tasks. Usually the MISSION mode is operated through the ground control station interface.
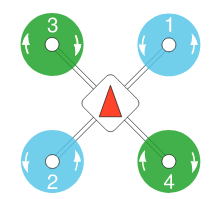
4. Propeller Mounting
For the sake of transportation safety, the propellers are not mounted on the airframe. We have to mount them properly according to the quadrotor configuration given below. Note carefully those rotation directions, and the wrench provided in the package can be used to save some efforts.
Caution
Caution: Users should always keep in mind that propellers must be removed during calibration process and other hands-on tasks.
5. Manual Flight in Position Mode
Hint
Instructions here are only applicable to Kerloud UAV in outdoor environment. For those with optical flow and vision-based localization settings, please refer to corresponding tutorials.
The position mode is the easiest way for users to get the machine fly. Basic steps are listed in sequence:
Make sure that the battery voltage is sufficient, and the voltage should be above 4.0v per cell (16v for a 4S battery).
Mount the battery ready with a cable, and make sure that it will not fall down during flight.
Be certain that all switches in the transmitter are in their initial position and the throttle stick is pulled down to minimum.
Power on with the battery.
Connect the telemetry with a computer, and start the QGC software. The QGC interface can provide full monitoring for the UAV.
Wait for the GPS to be fixed. Usually we can hear a beeping sound after 2-3 minutes if the local GPS quality is fine, and the main LED in the pixhawk will turn green.
Arm the UAV by pulling down the throttle and moving the yaw stick to the right, then we will hear a long beep from the machine. Please pay attention to channel differences between American and Japanese hands for the transmitter.
Switch to the position mode with the specified stick (e.g. channel 5). The QGC will indicate the position mode if the mode switching succeeds, otherwise it will provide warning messages. Failure in the mode switching are mostly due to GPS quality, sensor calibration, etc.
Push the throttle stick slowly above the middle level, and the UAV will take off smoothly.
Pull down the throttle stick slowly if we’d like the UAV to land.
Disarm the UAV after it lands by lowering down the throttle and moving the yaw stick to the left.