Indoor Localization System Setup with UWB Modules
Note: This tutorial is applicable for Kerloud UWB Suite only
1. Introduction
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) localization is a radio-based positioning method that measures the time-of-flight (ToF) of short radio pulses between anchors (fixed beacons) and tags (on the drone). By precisely estimating distances from multiple anchors, the system performs trilateration to determine the drone’s 3D position in real time. We provide the Kerloud UAV UWB suite for our customers as an alternative solution to vision-based methods and motion capturing facilities.
2. Hardware Setup
The setup of the localization system is quite straightforward. A minimal 5m*5m field is recommended for common users. Electromagnetic interference should be avoided as UWB signals can be volatile, so remember to keep a distance from suspicious interference sources for the field setup.
Detailed setup procedures are described in the user manual. For brevity, users are only required to setup the UWB anchors and conduct online calibration for one time. The scenario setup is depicted in the figure below.
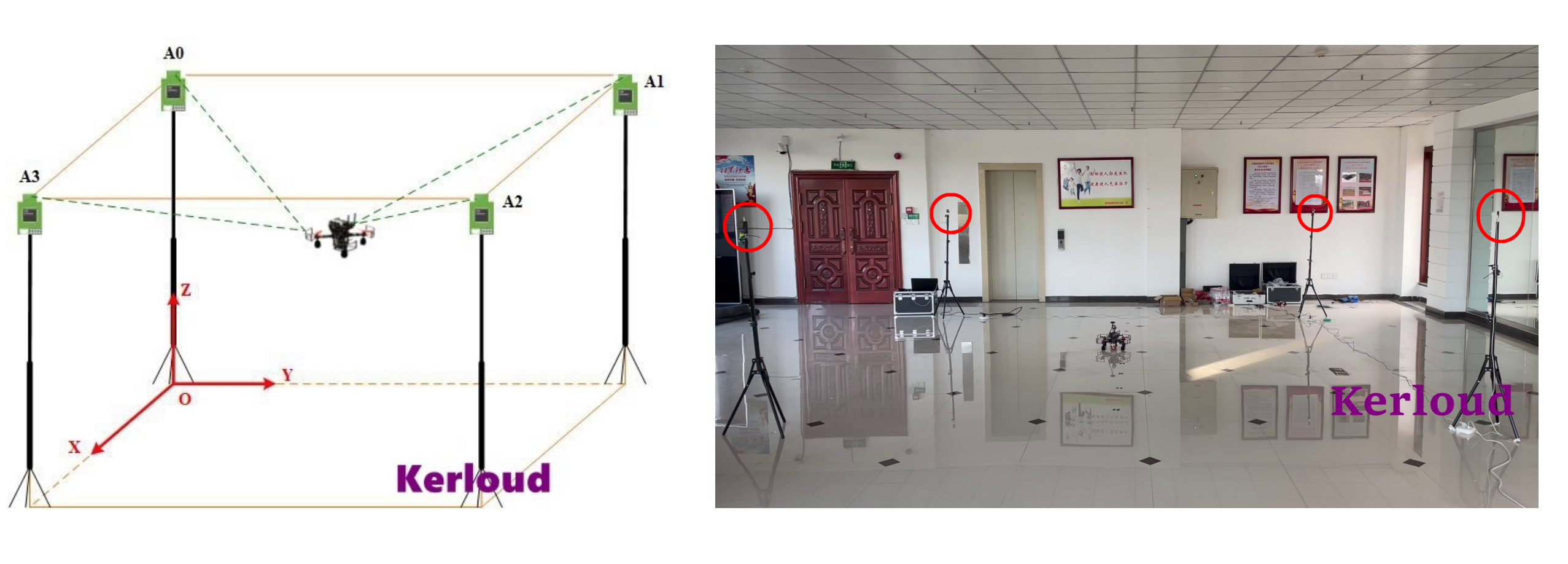
3. Installation from the Official Mirror
The UWB localization software packages are hosted in our official mirror https://mirror.cloudkernel.cn . Currently the software supports amd64 and arm64 architectures. Users are advised for follow the steps below for regular updates.
Download release files for Kerloud UAV uwb suite:
cd ~ && git clone https://gitee.com/cloudkernel-tech/dasa_release_files
Download deb files and install:
cd ~/dasa_release_files/install
bash download_deb_from_host.sh
bash install_all_deb.sh
The software package files will be installed to the onboard computer automatically.
Lock installed software packages for future apt update (recommended)
sudo apt-mark hold ros-melodic-mavros ros-melodic-mavlink ros-melodic-mavros-extras \
&& ros-melodic-libmavconn ros-melodic-dasa-visualization \
&& ros-melodic-mavros-msgs ros-melodic-nlink-parser ros-melodic-uwb-localization ros-melodic-loco-driver
4. How to Use
Measure the initial yaw angle of x axis in the ENU frame. Users can hold the UAV and rotate its heading to the x+ direction, and then record the yaw angle displayed in the Qgroundcontrol station. Denote the yaw value from Qgroundcontrol as yaw_ned.
Obtain the anchor coordinates from the NAssistant software for the Nooploop UWB modules.
Modify the content accordingly in the configure file in dasa_config.yaml under the directory dasa_release_files/scripts/single_case.
Please note that the variable yaw_dasa_x_axis_enu shall be computed from yaw_ned obtained in the 1st step.
# param: value # initial yaw angle of DASA x axis in the ENU frame, which can be observed from the QGC software, unit: rad, [-Pi, Pi] # we can lift the uav up and align its heading with the X+ direction, then the heading displayed in QGC is denoted as yaw_ned # formula: yaw_dasa_x_axis_enu = wrap2Pi(pi/2 - yaw_ned) yaw_dasa_x_axis_enu: 2.2 anchor_position: # numbers must in x.x format(i.e: 5.0), indexed by order, anchor0-3 # loaded only for nl setup, RFU frame by default - [ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] - [-0.13, 6.307, 0.0] - [ 2.857, 6.391, 0.0] - [ 2.981, 0.0, 0.0]
Copy the configuration file to the uwb_localization package installed in the system level.
cd ~/dasa_release_files/scripts/single_case sudo cp dasa_config.yaml /opt/ros/melodic/share/uwb_localization/config/
Finally, users can launch all necessary nodes for UAV localization including mavros, uwb driver and uwb_localization.
cd ~/dasa_release_files/scripts/single_case bash run_uav_default.sh
If everything goes well, the localization data can be revealed in the ROS topic /dasa/local_position/pose with the global frame defined by UWB anchors.
Note
More application examples can be found in the user manual delivered with our product.