Access the Autopilot with ROS Drivers
We provide two ROS packages to interface with the Pursuit autopilot as mentioned in the API section. They are intended for different use cases. The pursuit_driver is mainly for end-users with no programming basis, while the mavros package is devised for advanced developers to support extensible capabilities in the future such as IOT communication and robot simulation.
Method 1: pursuit_driver package
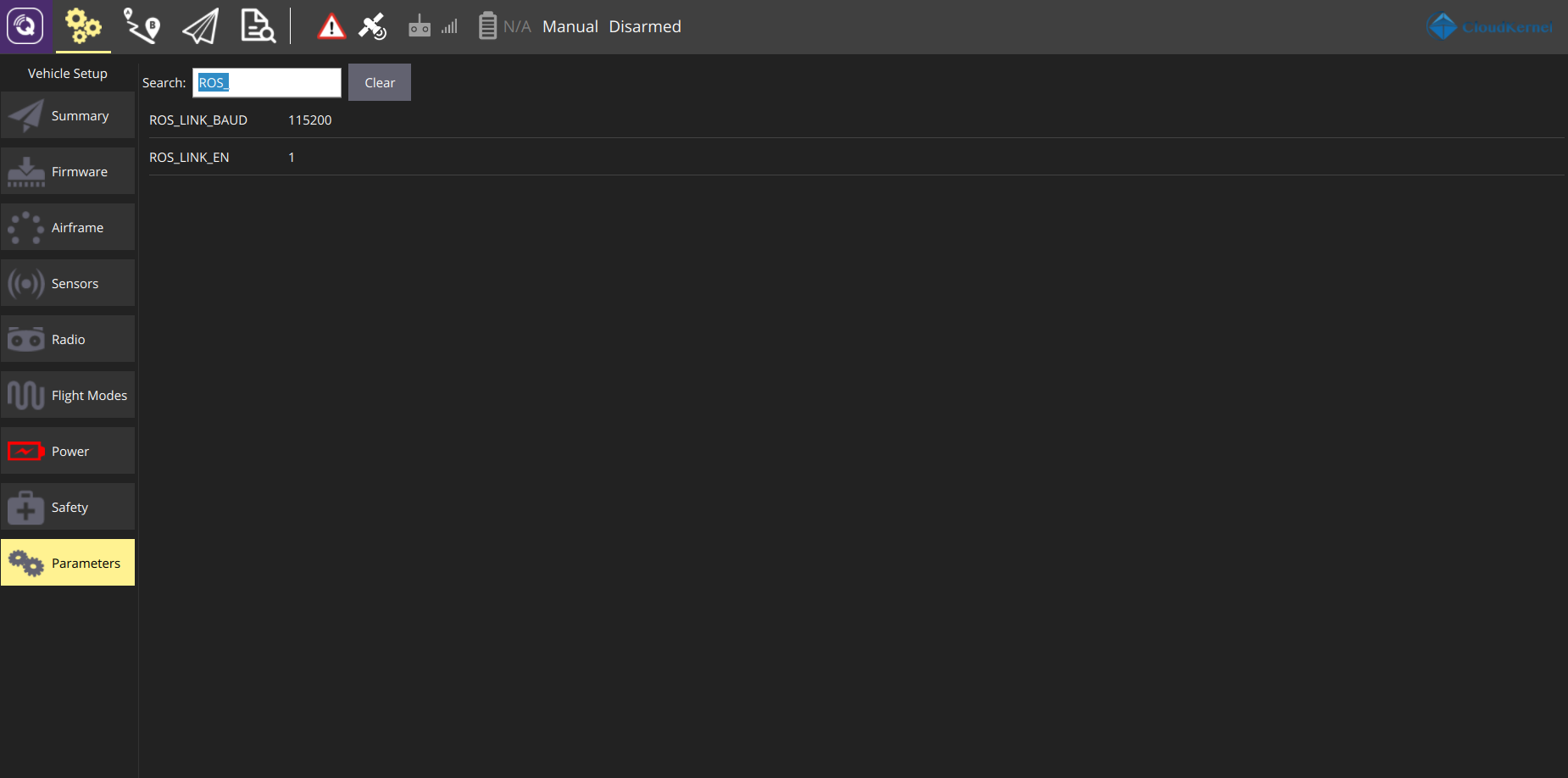
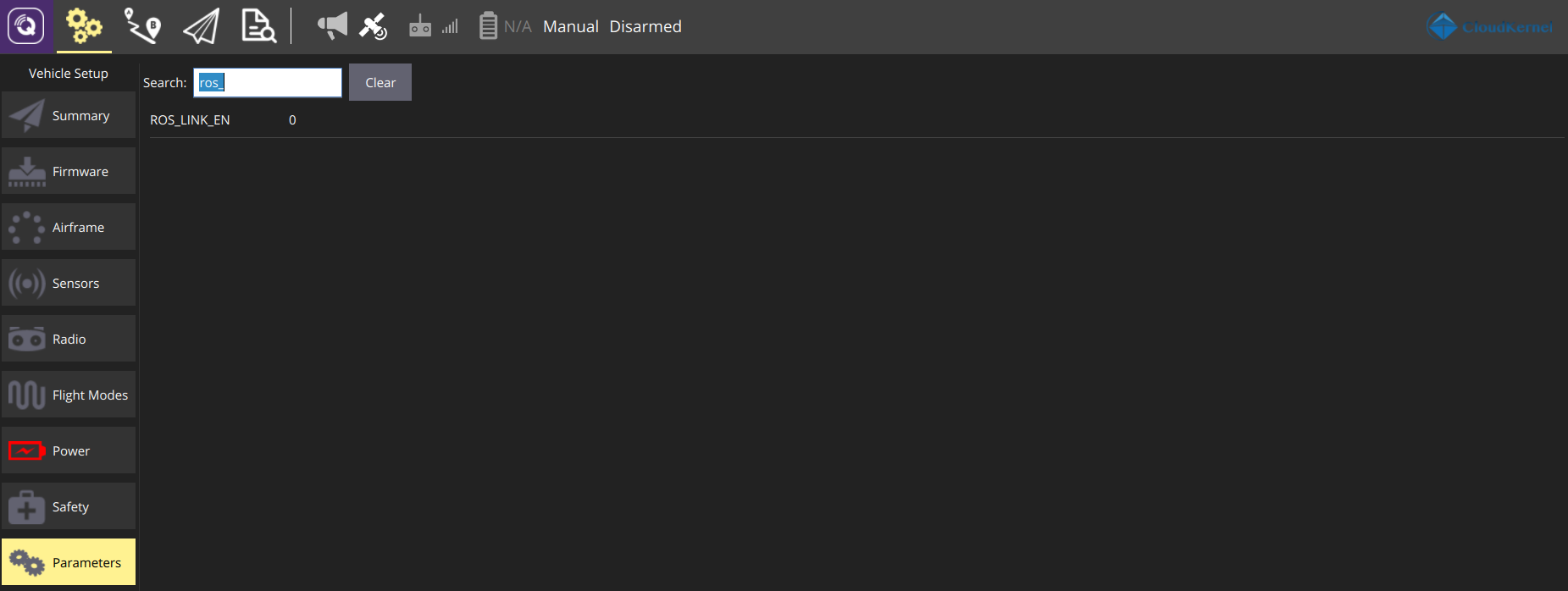
The interface with the pursuit_driver package is enabled by setting parameters in the QGroundcontrol software as:
ROS_LINK_BAUD=115200 #baud rate
ROS_LINK_EN=1 #enable the pursuit_driver interface
To start the pursuit_driver in ROS, users have to first locate the USB port for the autopilot with the command. In the official docker container we provide, the default USB port is /dev/ttyPursuit.
ls /dev/tty*

Then the pursuit_driver node can be brought up by:
cd ~/src/catkinws_nav
source devel/setup.bash
# launch with default port /dev/ttyPursuit
roslaunch pursuit_driver pursuit.launch
# or with the specified USB port, e.g. /dev/ttyUSB0
roslaunch pursuit_driver pursuit.launch serial_port:='/dev/ttyUSB0'
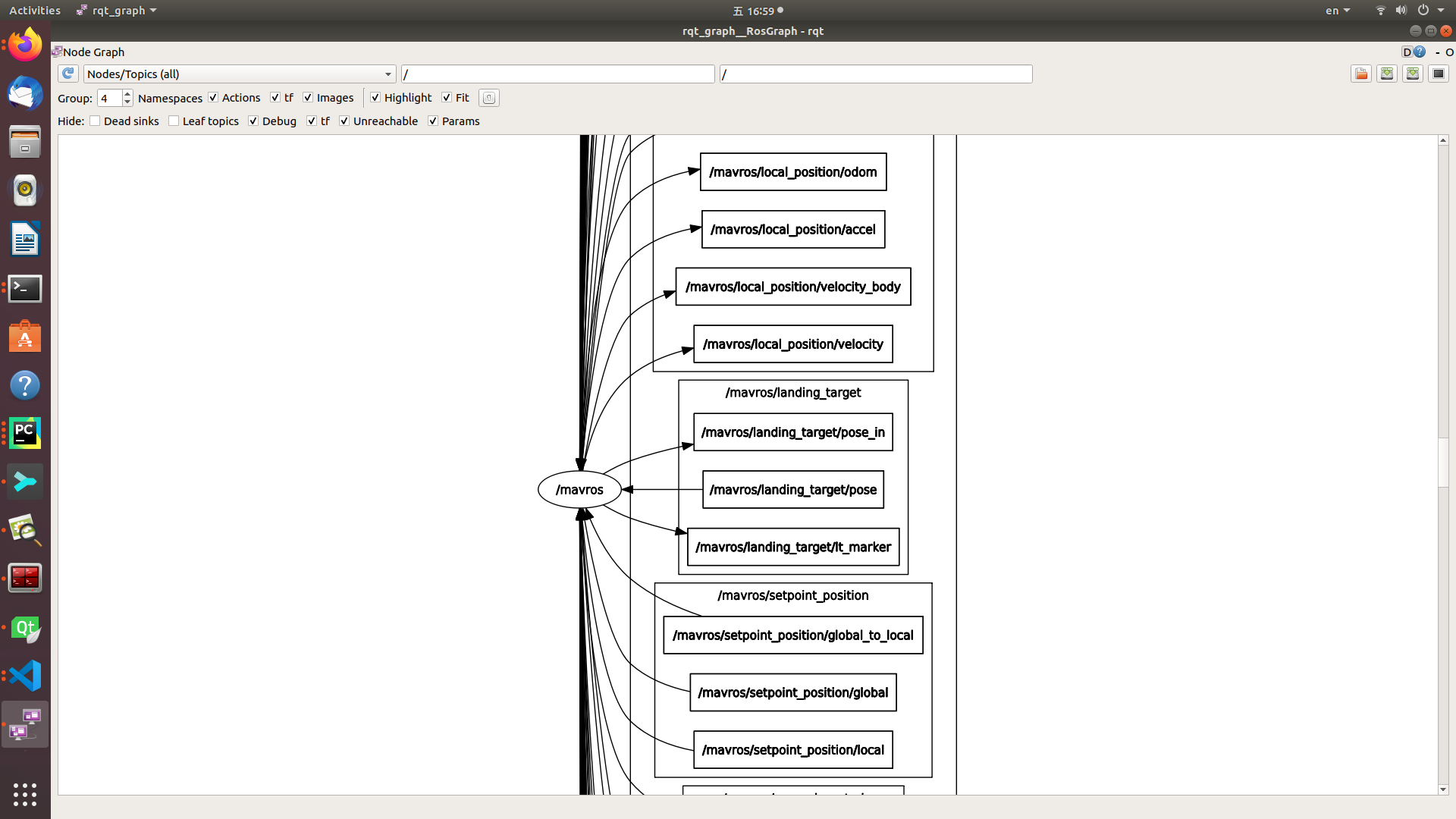
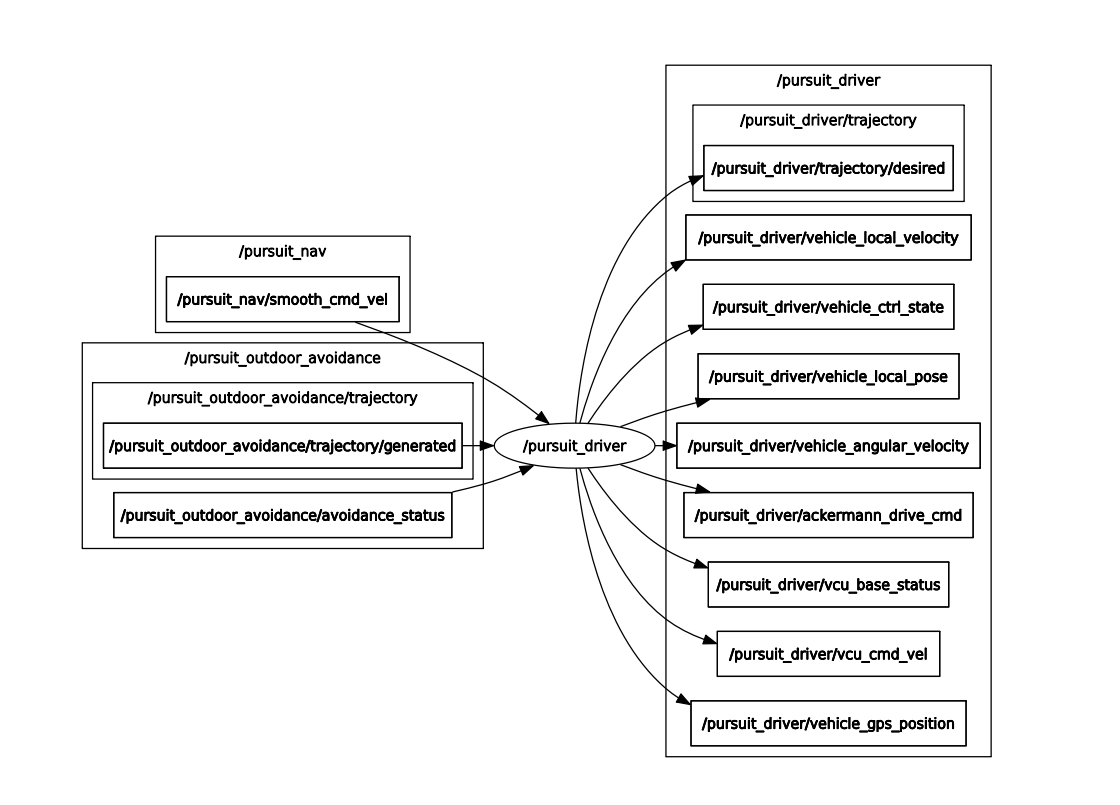
The rqt graph of the pursuit_driver node is shown below:
Method 2: mavros package
The interface with the mavros package is enabled by setting parameters as:
ROS_LINK_EN=0 # enable the mavros interface
SER_TEL2_BAUD = 921600 # the default baud rate for mavros interface, which is visible only after setting ROS_LINK_EN=0
Users have to locate the USB port for the autopilot in the same way as the pursuit_driver case, and then start the node with:
cd ~/src/catkinws_nav
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch mavros px4.launch fcu_url:='/dev/ttyPursuit:921600'
The partial view of rqt graph for mavros node is: